Implantation Failure Reasons: Understanding the Challenges in Embryo Implantation
Dealing with fertility treatments can be an emotional process, and one of the biggest challenges that many people face is implantation failure. This article provides an explanation for why an embryo may fail to implant in the uterus. The complicated factors—ranging from the quality of the embryo to the health of the uterus, hormonal impacts, genetic abnormalities, infections, and even ordinary lifestyle choices can have an impact on implantation.
What Is Implantation and Why Might It Fail?
Implantation is a crucial step in starting a pregnancy. It happens when a fertilized egg, which we call an embryo, finds its way to the lining of the uterus and attaches itself there. This connection is essential because it kick-starts the development of a pregnancy.
When implantation fails, the embryo doesn’t settle into the uterine lining, and the hoped-for pregnancy cannot take hold. Understanding why this happens is key to finding ways to improve the success rates of fertility treatments.
Embryo Quality
A major player in the implantation process is the quality of the embryo itself. Think of the embryo as the seed that needs the right conditions to grow. When it comes to implantation, a high-quality embryo is much more likely to thrive.
Genetic HealthEmbryos with healthy chromosomes have a better chance of implanting. Sometimes, chromosomal abnormalities or genetic issues, which might occur naturally or due to problems with the sperm or egg, can make implantation much less likely.
Cell DivisionHow quickly and consistently the embryo’s cells divide can be a good indicator of its viability. Embryos that follow the expected pattern of cell division generally have a higher chance of successful implantation.
Appearance (Morphology)Under the microscope, doctors assess the embryo’s structure and the way its cells are arranged. If an embryo looks abnormal or has poor cell structure, it may struggle to implant.
Advances in technology now allow fertility specialists to select embryos that appear to have the best chance of success. Yet, even when everything seems perfect on the surface, other factors might still interfere with implantation.
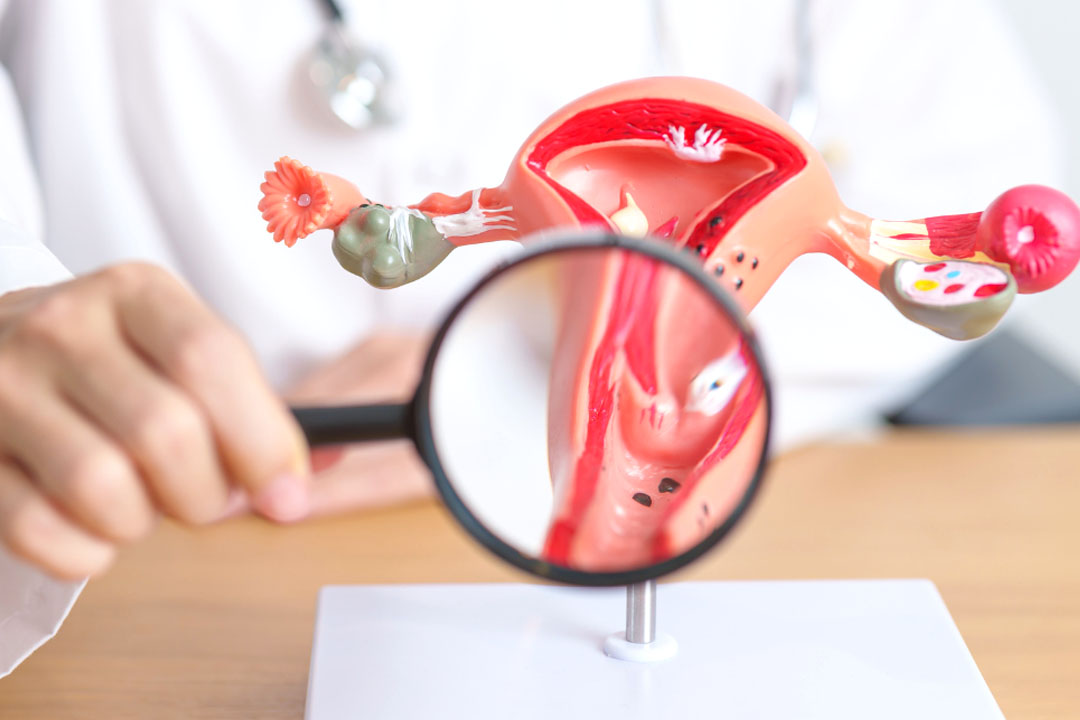
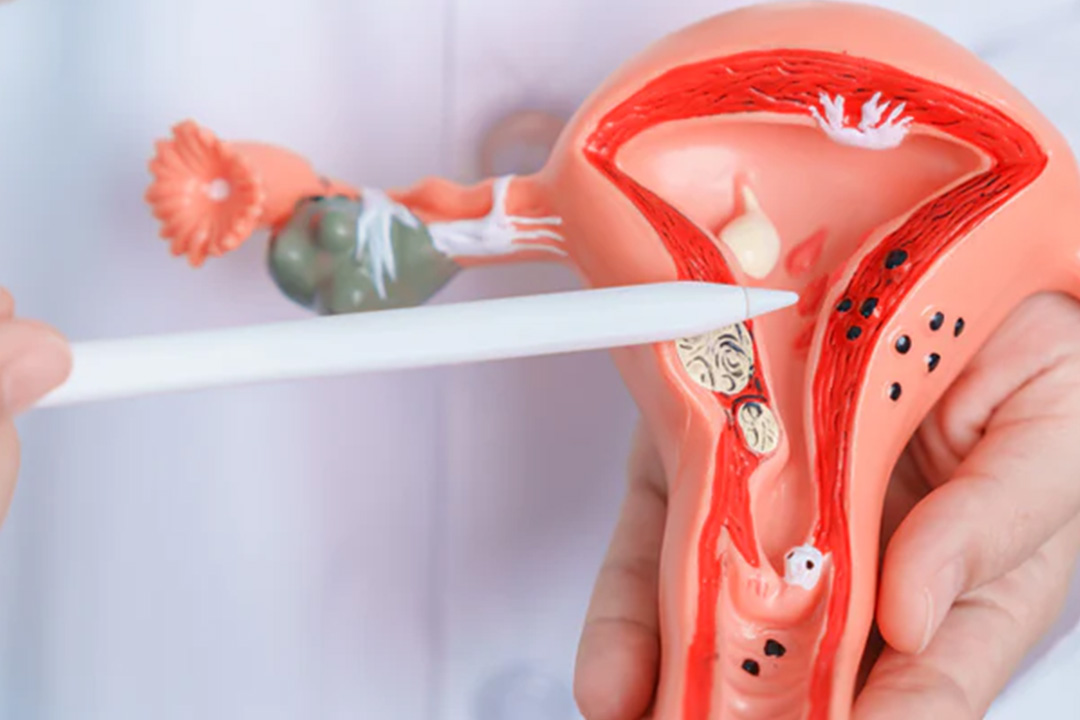
Uterine Environment
For an embryo to grow, it needs a nurturing environment. The uterus is that special place, and its lining must be in just the right condition for implantation. The following factors can have an impact on the uterine environment:
Endometrial ThicknessA thick, well-prepared uterine lining is like fertile soil for a seed. If the lining is too thin, the embryo might not have enough to latch onto.
Receptivity of the Uterine LiningBeyond just being thick, the uterine lining must be in a receptive state during a very specific window of time. This readiness is largely influenced by hormones and the changes they trigger in the uterine cells.
Structural IssuesSometimes, the uterus might have fibroids, polyps, or adhesions—scar-like bands of tissue—that can distort the inner surface. These irregularities can make it difficult for the embryo to find a good spot to attach.
Inflammation and InfectionsChronic inflammation or infections in the uterus can create a hostile environment. If the uterus isn’t calm and healthy, the embryo may simply find it too challenging to settle in.
Improving the uterine environment is often a key focus for fertility treatments. Doctors might use medications or other therapies to thicken the lining or reduce inflammation, giving the embryo a better chance of a successful implant.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones play a starring role in preparing the uterus for a new life. They set the stage for implantation, and even a slight imbalance can throw off the entire process. Key Hormones Involved:
Estrogen
Estrogen is like the builder of the uterine lining. It helps to thicken the tissue, preparing it for the embryo. Too little estrogen might mean the lining doesn’t develop fully, while too much can disrupt the timing and readiness of the lining.
Progesterone
Progesterone transforms the thickened lining into a cozy, supportive environment for the embryo. Without enough progesterone, the lining might not be as receptive, making it hard for the embryo to anchor itself.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
These hormones are essential for regulating the menstrual cycle and ovulation. If these hormones are out of balance, it can affect both the quality of the eggs and the timing of the uterine lining’s development.
Hormonal treatments are a common part of fertility care. By carefully monitoring and adjusting hormone levels, doctors can help create the ideal conditions for the embryo to implant.
The Immune System
Our immune system is a complex network that defends the body against foreign invaders. But in the case of pregnancy, the immune system sometimes sees the embryo as an unwelcome guest. How the Immune System Affects Implantation:
Autoimmune Reactions
In some cases, the immune system mistakenly attacks the embryo, treating it like an invader. This autoimmune response can prevent the embryo from implanting.
Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells)
These cells are part of our natural defense, but an excess of NK cells in the uterus can sometimes be harmful. They might attack the embryo, disrupting the delicate process of implantation.
Inflammatory Cytokines
Cytokines are proteins that help manage inflammation. However, if the levels of inflammatory cytokines are too high in the uterus, they can disturb the balance needed for the embryo to implant successfully.
Researchers continue to investigate how the immune system affects implantation, and in some cases, treatments may be recommended to calm an overactive immune response, making the uterus a friendlier place for the embryo.
Modern techniques such as preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) have become valuable tools. By screening embryos for genetic abnormalities before they’re implanted, doctors can improve the chances of selecting one that will successfully establish a pregnancy.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
It’s not just biology that plays a role in implantation; everyday lifestyle and environmental factors also have a significant impact. Small changes in your daily routine can sometimes make a big difference. Important Lifestyle Factors:
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals supports overall reproductive health. Deficiencies in key nutrients like folic acid, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids can adversely affect implantation.
- Stress: High stress levels can throw your body’s hormonal balance off track, making implantation more challenging. Managing stress through practices like meditation, yoga, or counseling can create a more supportive environment for fertility.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to lower rates of successful implantation. These habits can reduce blood flow and negatively affect the reproductive system.
- Weight and Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. Being either overweight or underweight can disrupt hormonal balance. Regular exercise and a nutritious diet can help optimize your body’s readiness for pregnancy.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to pollutants and chemicals in everyday life can also affect fertility. Minimizing contact with harmful substances can contribute to a healthier reproductive system.
- Uterine and Pelvic Conditions: Structural Challenges Beyond the embryo and the uterine lining, other conditions related to the uterus and pelvic region can also be significant factors in implantation failure.
Common Uterine Conditions
- Endometriosis: This is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside it. Endometriosis can cause inflammation, pain, and scarring, which may make implantation difficult.
- Adenomyosis: In adenomyosis, the inner lining of the uterus breaks through the muscle wall, which can thicken the uterine lining and make it less receptive.
- Fibroids: These noncancerous growths can change the shape of the uterine cavity and disrupt the smooth surface needed for an embryo to implant.
- Polyps: Small, benign growths in the uterine lining can sometimes block or interfere with implantation.
Conclusion
Implantation failure is a multifaceted challenge, and there’s rarely one single reason behind it. Whether it’s related to the quality of the embryo, the condition of the uterine lining, hormonal imbalances, immune system responses, genetic issues, infections, or lifestyle factors, every element plays a part. Often, it’s the interplay of several of these issues that can lead to a situation where the embryo fails to implant successfully.
The good news is that advances in medical science are continually improving our understanding of these processes. With modern techniques like preimplantation genetic testing, personalized medicine approaches, and a host of medical and surgical interventions, there are more options than ever for addressing the underlying causes of implantation failure.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.