What is Necrozoospermia? Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment and More
Necrozoospermia is a reproductive condition where a large percentage of sperm cells in a semen sample are non-viable or dead. In simple terms, necrozoospermia means that most of the sperm present are immotile and cannot swim or fertilize an egg.
Necrozoospermia is defined by a significantly high proportion of non-motile sperm, while some immotile sperm in a sample can be normal.
This condition stands apart from other sperm abnormalities such as asthenozoospermia, which deals with reduced sperm motility but not necessarily complete immobility.
The term 'astheno necrozoospermia' sometimes appears when there is a combination of asthenozoospermia and necrozoospermia characteristics.
Understanding what necrozoospermia is and how it differs from related issues like oligo necrozoospermia (low count of non-motile sperm) or complete necrozoospermia (all sperm are non-viable) is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
The percentage of immotile or dead sperm is a key factor in diagnosing necrozoospermia. Research shows that when more than 40-50% of sperm are non-motile or dead, the condition may be present. This significant presence of non-viable sperm can make natural conception difficult.
What is Necrozoospermia?
Necrozoospermia is a type of sperm motility disorder that specifically points to the presence of a high percentage of immotile or dead sperm in semen.
This condition is distinct from other abnormalities like teratozoospermia, which involve abnormal sperm morphology, because necrozoospermia focuses solely on the vitality of sperm cells.
The term 'necrozoospermia definition' guides clinicians to measure the number of live versus dead sperm. Typically a diagnosis can be made if the percentage of non-motile sperm crosses a certain limit, usually around 40-50%. This high percentage points towards serious underlying issues in sperm production, motility, or survival.
The condition might present as complete necrozoospermia when all sperm in the sample are immotile. In contrast, oligo necrozoospermia involves both a low sperm count and a high percentage of dead sperm.
Differences from Other Sperm Abnormalities
Asthenozoospermia describes reduced sperm motility but it does not necessarily mean the sperm are dead. In necrozoospermia, the primary issue is the death of sperm cells, which results in complete immotility.
Astheno necrozoospermia refers to cases where there is both a reduction in motility and an increase in non-viable sperm.
Teratozoospermia is another sperm abnormality that deals with the shape and structure of sperm cells. Abnormal morphology can impact fertility but the key feature of necrozoospermia is the lack of viable sperm capable of fertilizing an egg, regardless of their shape.
Causes of Necrozoospermia
The causes of necrozoospermia are multifactorial. Understanding necrozoospermia causes and treatment requires a deep dive into various contributing factors. Some common causes include:
- Problems within the testicles such as trauma, infections, or surgery can result in defects in sperm production. These conditions can affect spermatogenesis, leading to a high number of non-viable sperm.
- Certain genetic mutations or chromosomal anomalies may affect sperm development or lead to early sperm death. Genetic testing can sometimes uncover these abnormalities.
- Long-term exposure to toxins, radiation, heavy metals, or extreme heat can damage sperm cells. Lifestyle choices like smoking and excessive alcohol use are linked with an increased risk of necrozoospermia.
- Reproductive tract infections, including sexually transmitted infections, can damage sperm directly or through inflammation. Inflammatory mediators can alter the environment of the reproductive tract, adversely affecting sperm vitality.
- Diseases such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or hormonal imbalances can impact sperm health. For example, low testosterone levels or thyroid issues may hinder proper sperm production.
Studies have found that the epididymis, a crucial site for sperm maturation, can be dysfunctional in necrozoospermia individuals.
Dysfunctions in the epididymis may expose sperm to oxidative stress, leading to their damage or death. Oxidative stress is a condition where there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, resulting in cellular damage.
In addition, exposure to high temperatures can impair spermatogenesis. Prolonged heat exposure due to environmental conditions, fever, or lifestyle factors such as wearing tight clothing can lead to thermal stress on the testes.
This heat stress interferes with the normal production of sperm and can result in a higher proportion of non-viable sperm.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Environmental toxins play a significant role in necrozoospermia. Research indicates that long-term exposure to substances like pesticides, tobacco, and cannabis can induce necrozoospermia.
For instance, cannabis use has been linked to impaired mitochondrial function in sperm, reducing energy production and ultimately leading to sperm death.
Similarly, obesity is associated with increased testicular heat and hormonal imbalances. Both of which can affect spermatogenesis. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through proper diet, exercise, and avoiding toxic exposures can thus help in reducing the risk of necrozoospermia.
Diagnostic Approach
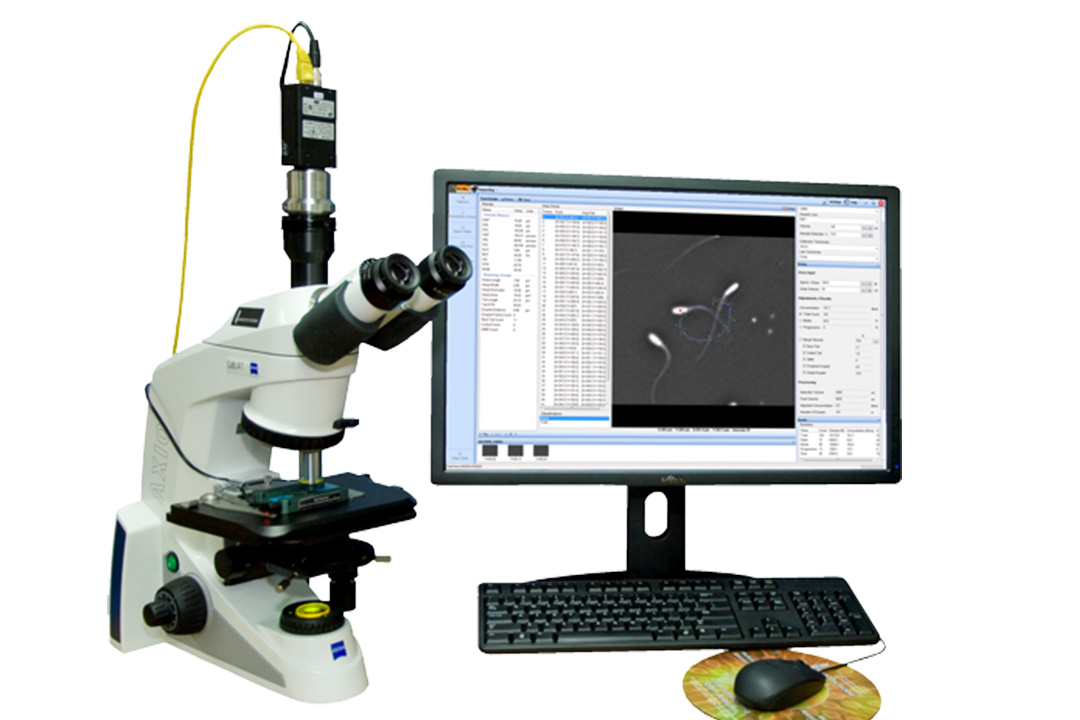
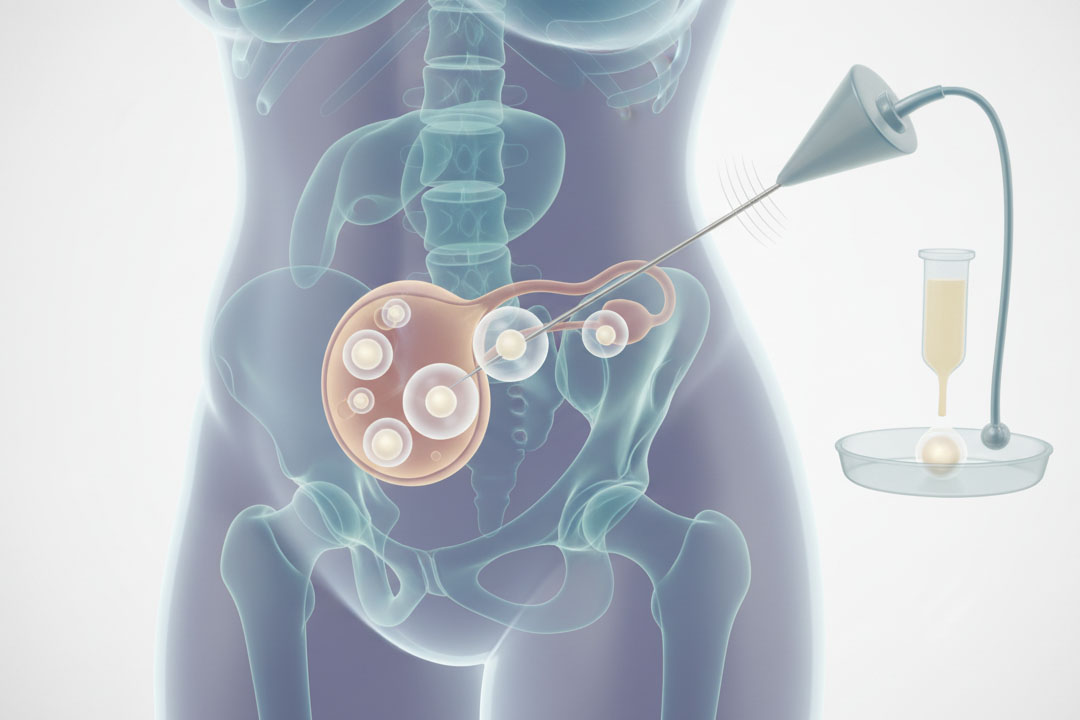
The first step in treating necrozoospermia is to do a complete semen analysis. This test examines sperm count, motility, and morphology, with a focus especially on determining the percentage of nonviable sperm.
Knowing the necrozoospermia % helps doctors to determine the severity of the problem. Hormonal tests, genetic testing, and infections or varicoceles may be performed as follow-up evaluations.
Imaging methods may be used to discover structural abnormalities in the reproductive system. Ultrasound can reveal varicoceles or blockages that interfere with sperm transfer. Blood testing can rule out systemic conditions or hormonal abnormalities that cause necrozoospermia.
Treatment for Necrozoospermia
Treatment for necrozoospermia treatment depends heavily on the underlying cause. When a specific cause is identified, targeted interventions are pursued:
- Simple changes like quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged heat exposure can improve sperm viability. These changes may not reverse necrozoospermia entirely but can reduce the severity.
- If infections are present, appropriate antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed. Hormone therapy might be necessary for those with hormonal imbalances affecting sperm production. In cases where immune responses are identified, immunosuppressive therapy might be considered to reduce antisperm antibodies.
- Structural issues such as varicoceles may require surgical correction. Varicocelectomy, the surgical repair of varicoceles, can sometimes improve sperm quality and decrease necrozoospermia. Other procedures may address blockages or injuries within the reproductive tract.
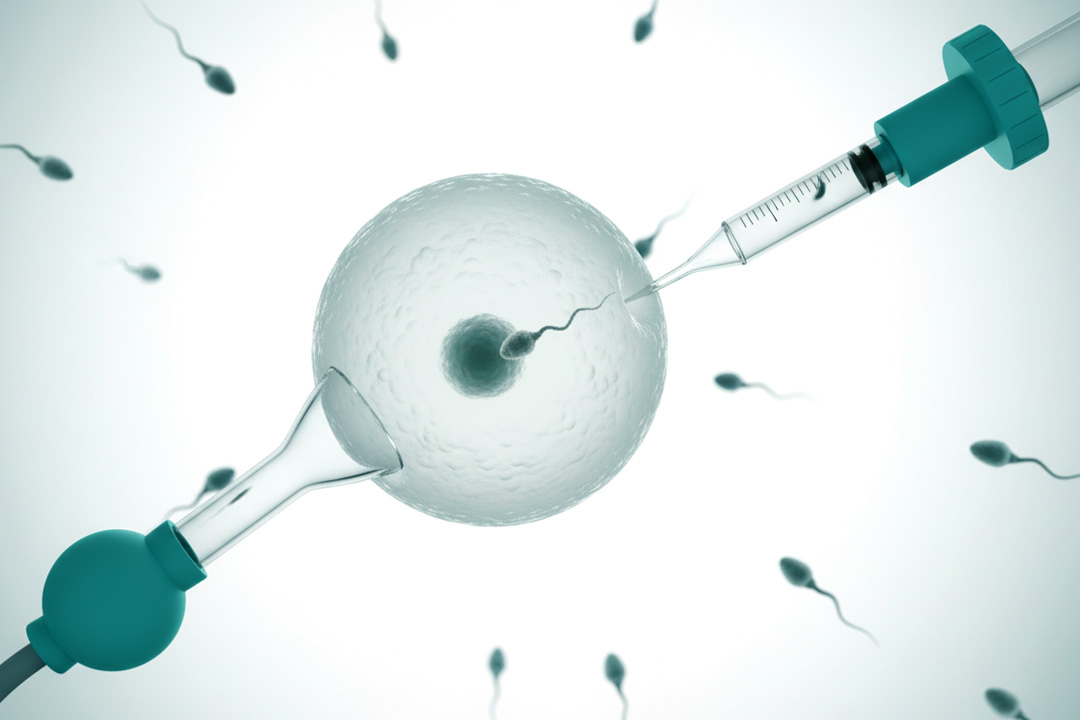
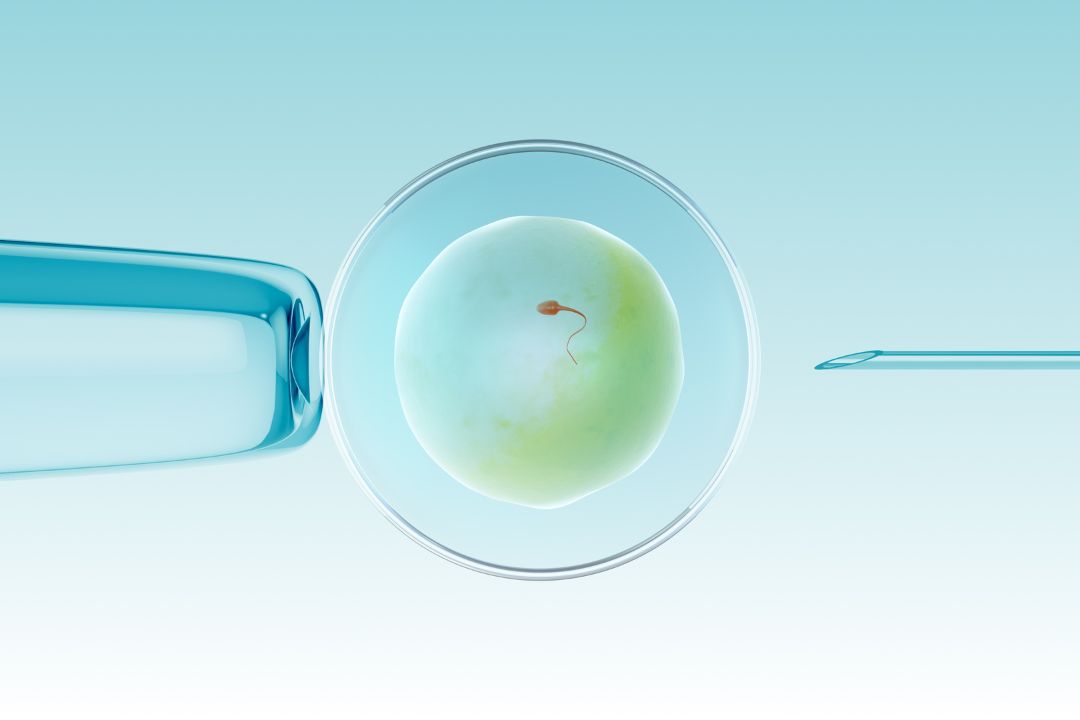
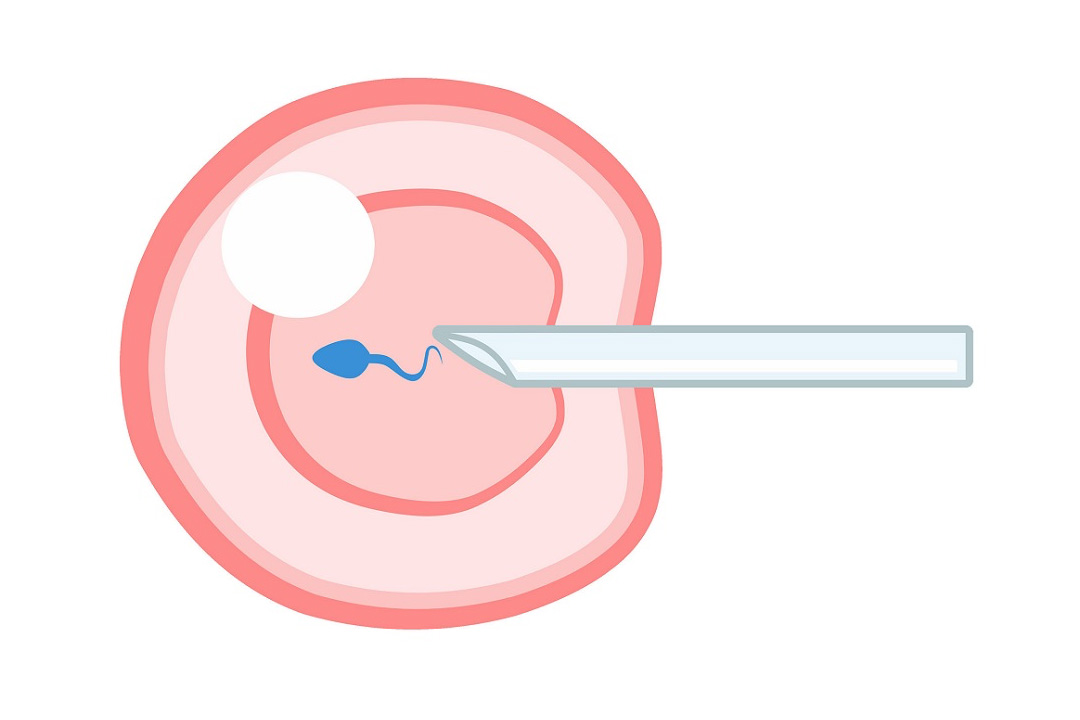
- For severe cases where natural conception is unlikely, couples may turn to assisted reproductive techniques. IVF andintracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) are common methods.
In ICSI, a single sperm is injected directly into an egg, bypassing the need for motile sperm. This technique is often used when faced with complete necrozoospermia, where no viable sperm can fertilize an egg naturally.
Advancements in genetic screening also allow for earlier detection of genetic factors contributing to necrozoospermia.
As the understanding of the molecular basis of sperm death improves, more targeted treatments can be developed. These treatments may range from gene therapy to more refined hormonal treatments that specifically address the underlying cause.
Clinical Cases and Observations
Clinical observations show that necrozoospermia can be quite complex. Patients suffering from spinal cord injuries, for example, are more likely to develop necrozoospermia.
This might be caused by a variety of causes, including decreased thermoregulation in the genital region and a greater risk to urogenital infections.
Also, prolonged sitting, which is common among wheelchair users, can increase scrotal temperature and interfere with sperm production.
The diagnosis of necrozoospermia can be stressful for couples. Psychosocial help is necessary for couples managing reproductive treatments and the emotional strain that comes from many failed conception attempts.
Conclusion
Necrozoospermia is a severe condition with a high percentage of non-viable sperm cells in a semen sample. Unlike other sperm abnormalities, necrozoospermia specifically refers to sperm death and complete immotility. It makes natural conception challenging.
Through lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, surgical repairs, and assisted reproductive technologies, many individuals with necrozoospermia can find ways to successful conception. Ongoing research aims to better understand the biological mechanisms underlying the condition.
By integrating clinical insights with advancing scientific knowledge, healthcare providers continue to develop strategies to improve the situation for those affected by necrozoospermia.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.